Spotted Hyena
About the Spotted Hyena

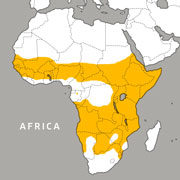
Geographic Range:
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Hyaenidae
Genus: Crocuta
Species: crocuta
Spotted hyenas are known for their distinctive vocalizations used for communication, earning them the nickname, "laughing" hyenas. Vocalizations include cackles, howls, yells, whoops and other sounds which are inaudible to humans. Whoops are used to gather or alert clan members, while the laugh or giggle is actually a submissive gesture. Spotted hyenas also use body language and posturing to communicate with each other.
Committed to Conservation
Zoo New England participates in the spotted hyena Species Survival Plan. By sharing research and knowledge, participating institutions work together to establish guidelines that best ensure the health of captive populations, and with success, the survival of endangered species.
Hyena Facts
Appearance:
Spotted hyenas is a long-limbed animal with yellowish-brown fur and oval spots. Though similar in appearance to canines, hyenas are more closely related to felines. Their front legs are longer than their back legs, giving them a hunched look. Hyenas have large eyes and ears and a short, upright mane running along the back of their neck. Their muzzles are thick and their teeth are short and powerful. Hyenas have strong jaws that allow them to break bone, and they can digest almost all parts of a carcass. Coarse hair and hooves that can't be digested are coughed up in a pellet.
Size:
Weight: 100 to 150 pounds
Height: 2 to 3 feet at the shoulder
Length: 3 to 5 feet
Diet:
Though they scavenge for carrion, hyenas get most of their diet through active hunting. Hunting alone, hyenas prey upon smaller mammals, birds and reptiles. When hunting in a group, they'll tackle larger prey such as the gazelle, wildebeest and zebra. Hyenas supplement their diet with vegetation.
Mating/Reproduction:
Spotted hyenas usually breed once per year, and they don't have a constant breeding season. After a 110- to 120-day gestation period, females give birth to one to three pups. Pups reach sexual maturity after 2 to 3 years of age, with males maturing sooner than females.
Behavior:
Spotted hyenas live in large groups called clans that are dominated by alpha females. Females of a clan are related, but males aren't. When young males mature, they disperse and join neighboring clans. Each clan defends its territory against other hyena clans. The territory's center is typically kept at high ground. Here, hyenas build a den for mothers and cubs.
Spotted hyenas use a variety of vocalizations to communicate. Such communications include cackles, howls, yells and whoops. Some of these vocalizations are inaudible to human ears.
Habitat/Range:
Spotted hyenas live in a wide variety of habitats including savannahs, semi-deserts, open woodlands and mountainous forests. They range throughout sub-saharan Africa except for the Congo rainforest, southern Africa and Madagascar.
Median Life Expectancy:
22.3 years
Fun Fact:
- Spotted hyenas are the largest of four hyena species which also include striped and brown hyenas and the aardwolf.
- Hyenas are a top predator with one of the most powerful jaws for an animal of their size
You Can Find This Animal in the Kalahari Kingdom
Fun Fact
Although hyenas look like dogs, they're actually more closely related to cats!
You May Also Like
At Franklin Park Zoo:
At Stone Zoo:



















