Appearance:
Chacoan peccaries have dark, bristle-like fur with dark stripes across their backs and white fur on their shoulders. Chacoan peccaries have 3 hind toes; other species have 2.
Size:
41 inches long on average
68-88 pounds on average
Diet:
Fruits and other plants; cacti form the bulk of the peccary’s diet and provide the peccary with 90% of its water needs. The peccary has specialized kidneys to break down acid in cacti, and its two-chambered stomach is well suited to digest tough foods.
Reproduction:
This wild pig's breeding period runs from April through June. They reach sexual maturity between 16-24 months and have a gestation period of 151 days. Females give birth to one litter per year, usually in September or October. Litters typically consist of 1-4 piglets (usually only 2-3).
Behavior:
Chacoan peccaries use scent marking to keep the herd together, recognize one another, and mark territories. They're known for their ability to make pathways through virtually impenetrable areas of thorny bush.
Peccaries are active from dawn to dusk and feed throughout the day. They tend to be less active in the middle of the day, when it's the hottest. They sleep in groups and use a nighttime resting site only 2-3 nights in a row. Herds, likely extended family groups, consist of males and females and range from 1-10 individuals. The Chacoan peccary is less aggressive than other peccary species.
Role in their habitat:
Chacoan peccaries are prey to mountain lions and jaguars. By reason of a fruit diet, they are major contributors to seed dispersal.
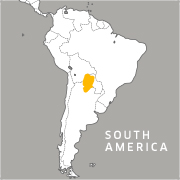
Habitat/Range:
Chacoan peccaries are native to hot, dry forests and grasslands in Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay.
Median Life Expectancy:
Unreported
Fun Facts:
- The Chacoan peccary was not recognized as a living species until 1975, making it one of the most recently discovered large mammals.
- Peccary, a name which originated with the Brazilian Tupi people, means “animal which makes many paths through the woods."