Blue and Yellow Macaw
Ara ararauna
| ⚠️ Animal Alert The macaws are kept indoors when temperatures drop below 60 degrees. Visit our Winter Visits page to learn more about the amazing animals you can see during the winter! |
About the Blue and Yellow Macaw

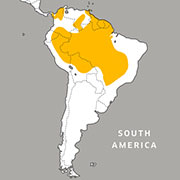
Geographic Range:
Class: Aves
Order: Psittaciformes
Family: Psittacidae
Genus: Ara
Species: ararauna
Blue and yellow macaws have turquoise blue bodies, gold stomachs, and a patch of green on the top of their heads. Their bright coloration provides camouflage, helping them blend in with leaves and bright fruits. The macaw’s powerful black beak is designed to crush or open even the hardest nuts and seeds. In fact, its beak is powerful enough to snap a broomstick in half!
Blue and Yellow Macaw Facts
Appearance:
Blue and yellow macaws have turquoise blue bodies, gold stomachs, and a patch of green on the top of their heads. They have a bare facial patch with small, lined feathers that cross their face. Their bright coloration provides camouflage, helping them blend in with leaves and bright fruits. The macaw’s powerful black beak is designed to crush or open even the hardest nuts and seeds. In fact, its beak is powerful enough to snap a broomstick in half.
Strong toes give macaws a good grip on perches and also come in handy for "holding" favorite foods, like nuts, fruits and bugs.
Size:
- Length: 30 – 34 inches
- Weight: 2 – 3 pounds
- Wingspan: 3 feet
Diet:
Seeds, nuts, fruits, plants and small lizards.
Reproduction:
Blue and yellow macaws generally mate for life. The brighter and bolder the male’s colors are, the better his chances are of finding a mate. They have been known to breed at 3-6 years of age during any part of the year, nesting in dead palms. Their clutch consists of two to three eggs which incubate for 16-24 days. One chick is dominant and gets most of the food, while the others perish. Chicks will stay in the nest for about three months and leave their parents after 1-2 years.
Behavior:
These birds are generally seen in pairs, but they can form flocks of up to 30 birds. Macaws are diurnal (active during the day), flying from roosting sites to feeding grounds every morning, and returning just before sunset. They’re wary birds, often flying into the air and screeching at any sign of danger. These birds communicate with screams, squawks and squeaks. They’re known to “scream” for attention and make other loud noises; these screams can be heard two miles away.
Habitat/range:
Macaws live in Venezuela, Peru, Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Panama. They can be found in rainforests, woodlands, and tall palms, especially near swamps and rivers.
Role in their habitat:
Macaws serve an important role in their ecosystem by dispersing seeds and nuts throughout their territory.
Median Life Expectancy:
In the wild: 30 – 35 years
In captivity: 50+ years
Fight Wildlife Trafficking:
Catching and selling wild macaws illegally is called trafficking. Many of the birds die or get sick. Support laws against trafficking and don't buy macaws as pets.
You Can Find This Animal in the Caribbean Coast
A bird to be heard!
These birds communicate with screams, squawks and squeaks. The mouthy macaw's screams can be heard two miles away!
You May Also Like
At Franklin Park Zoo:
At Stone Zoo:












